The quality of corrugated cartons depends on the binder used, depending on the quality of the paper and the processing process. Therefore, the adhesive plays a key role in the production of corrugated boxes.
At present, most of China's carton factories are small-scale enterprises without drying equipment. Therefore, although the use of sodium silicate as a corrugated paperboard adhesive has the disadvantages of large alkali, easy moisture absorption and panthelinization, and large corrosiveness, and the country strictly restricts its use, it is due to its low cost and rapid drying characteristics. Most companies still use sodium silicate as a binder rather than using a starch binder that is relatively slow to dry. Therefore, how to develop a starch-based adhesive that has a drying rate equivalent to that of sodium silicate as quickly as possible and that is inexpensive is an urgent problem to be solved. After more than 10 years of research and development, we have developed a fast-drying starch binder, and after years of use by packaging enterprises in Hunan, we have proved that the production process is simple, the quality is stable, the storage period is long, the gelling is not easy, the drying speed and the silicic acid Sodium is equivalent, the cost per ton of adhesive is about 350 yuan, and the production cost is 25-30% lower than that of sodium silicate. The cartons made with the adhesive were tested by the Hunan Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau, and the indicators exceeded the standards for export packaging cartons.
First, the oxidation reaction mechanism of the binder
Oxidized starch has high paste stability, greatly reduced retrogradation, less tendency to coagulate into gels, high flowability, good transparency, and strong adhesive force. The adhesive we developed was at room temperature, with nickel sulfate as the catalyst and sodium hypochlorite as the oxidant. After the starch oxidation reached a certain depth, other auxiliary materials were added to make the oxidized starch paste. The sodium hypooxygenate decomposes in the aqueous solution under the action of heat or a catalyst, and releases the initial ecology [O] with a strong oxidizing ability. The starch undergoes an oxidation reaction under the action of the initial ecology [O], and the oxidation causes the starch glucose. The oxime bond between the base ring is broken and degraded, resulting in a decrease in the degree of polymerization, a decrease in the molecular weight, and an increase in the water solubility and affinity, so that a binder containing a relatively high solid content can be prepared and the drying ability can be improved. At the same time, the hydroxymethyl groups in the starch become aldehyde groups due to oxidation. By further oxidizing, it is also possible to make the moiety hydroxyl, so that the number of hydroxyl groups having a strong binding force with the paper fiber increases, thereby greatly increasing the adhesion of the oxidized starch. In addition, due to the aldehyde groups generated after oxidation, the fermentation and biodegradation of starch by microorganisms are inhibited, and the binder produced improves the anti-corrosion and anti-mildew properties.
The rate of oxidation increases with temperature and the amount of oxidant. At room temperature, nickel sulfate is added as a catalyst in order to increase the rate of oxidation reaction, and the oxidation reaction can be performed even at a temperature lower than 10°C. For self-made small and medium-sized enterprises, due to the small amount of daily adhesive, in order to reduce production costs, the amount of oxidants can be appropriately reduced to extend the oxidation time to reach the depth of oxidation. It can usually be left to oxidize for about 12 hours at night.
Second, the production of adhesives
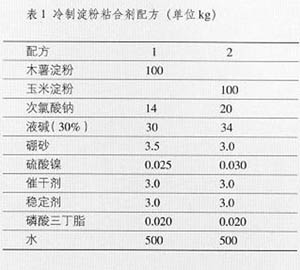
1. Raw materials and formula starch: available corn starch or tapioca starch, color white, more than 100 mesh, water content below 14%, with protein less than 0.5%, no mildew, no agglomeration.
Liquid caustic soda: Industrial products with content of 30% ± 0.02 (solid base can also be used).
Oxidizer: Industrial grade sodium hypochlorite with 10% effective chlorine content.
Oxidation catalyst: Industrial-grade nickel sulfate, formulated as a 0.5% aqueous solution when used.
Cross-linking agent: Industrial-grade borax, used as a 2% aqueous solution in cold water.
Additives: Sulphur, nitrogen, phosphorus, organic substances and other substances, are all industrial grade.
The basic recipe is shown in Table 1.
2. Major equipment and process flow
The main equipment is reactor and electric mixer. Because the reaction process is carried out at room temperature and under weak alkaline conditions, it is not corrosive, and it can be welded with thin steel plates or covered with brick cement. The motor power can be 3-5 kW depending on the output size and the stirring speed is 60-70 rpm. The entire production process takes place in the reactor.
The adhesive production process is shown in Figure 1.

3, production methods
Oxidation: Add 100 kg of water to the reactor, add 14 kg of sodium hypochlorite under constant stirring, add 100 kg of cassava starch, stir well, and finally add 25 g of 0.5% nickel sulfate solution, stir for about 5 minutes, and allow it to oxidize overnight.
Gelatinization: Add 100 kg of water first. After mixing, add 30 kg of a 10% solution prepared in advance with 30% liquid caustic soda, and mix for about 20 minutes to make it a homogeneous transparent pale yellow gel. Add 3 kg of driers with 5% concentration and 3 kg of stabilizer.
Cross-linking: add 3.5 kg of borax with stirring and pre-form 2% solution and proper amount of water. Use 4 cup to measure the viscosity as 40-50S. Finally add antifoam agent tributyl phosphate 20% as foam. Grams around.
Third, the main factors affecting the quality of adhesives
The quality of cold catalyzed oxidized starch adhesives is related to many factors. The appearance of a good quality adhesive must be clear and transparent, slightly yellowish, non-foaming, suitable viscosity, high stability, long shelf life, fast drying, and strong adhesion. The following only discusses several factors that affect quality.
1. Oxidizer dosage and oxidation time. The relationship between the oxidation temperature Sodium hypochlorite is a strong oxidant. For a certain amount of starch, under the same conditions, the amount of oxidant increases, and the oxidation rate will increase. That is, the viscosity of the adhesive will decrease. Therefore, the appropriate amount of oxidant should be determined according to the actual production conditions. If it is necessary to shorten the oxidation time, the amount of oxidant may be appropriately increased. When the oxidation depth is reached, the terminator sodium thiosulfate may be added to terminate the reaction. SMEs can make their own use, can use the evening time for oxidation, in order to prolong the oxidation time, which can reduce the amount of oxidants, reduce raw material consumption, to achieve the purpose of reducing costs.
The temperature of the oxidation reaction also affects the speed of the oxidation reaction. The higher the temperature, the faster the oxidation reaction, and the other conditions are the same, the smaller the adhesive viscosity is. Therefore, according to different temperature conditions, control the amount of different oxidants and oxidation time.
2. Effect of sodium hydroxide dosage
In cold-formed starch, sodium hydroxide acts as a pasting agent to form a homogeneous, transparent, viscous starch paste with water-insoluble oxidized starch and water. This is because after the addition of sodium hydroxide, its hydroxide is combined with the hydroxyl group in the starch molecule, breaking the hydrogen bonds between the starch macromolecules and the original hydroxyl groups in the molecule, thereby swelling and gelatinizing the macromolecules. In addition, sodium hydroxide changes the carboxyl group in the oxygen molecule to a sodium carboxylate group, which increases the solubility with water. At the same time, sodium hydroxide stabilizes the amylose solution under anaerobic conditions, making the adhesive less likely to gel. However, sodium hydroxide is not added as much as possible, and its amount and temperature must be strictly controlled. When the amount is too large, paper fibers are destroyed due to high alkalinity, and when the air humidity is high, moisture absorption is yellowish. On the other hand, when sodium hydroxide is added, the concentration cannot be too high. Due to the high concentration, the reaction during the gelatinization is violent, and the saccharification is likely to occur, which causes the squeezing machine to squeezing the rubber, and the saggers appear on the corrugated peak of the corrugated stencil, thereby causing the phenomenon of Cardboard is open and difficult to dry. Generally, the amount of sodium hydroxide added (solid) is 9-10% of the amount of starch, and the concentration when added is 10%.
3. The effect of the amount of hydroxyborax
Borax is used as a cross-linking agent. Boron and oxygen are the central ions when it is hydrolyzed in aqueous solution. It can combine with hydroxyl and carboxyl groups in the binder to form a ligand, forming a multi-nuclear complex with a network structure, thereby increasing the viscosity. . And can be better fixed on the surface of paper with carboxyl groups, increase the initial adhesive force of the adhesive, make the resulting film firm, improve the ability of water resistance and natural drying. However, borax can not be added too much, otherwise it will make the adhesive layer brittle, resulting in degumming.
4. The role of additives
In adhesives, additives are added for the purpose of quick drying, stabilization, and anti-gelling to extend the shelf life. We added an inorganic double salt and water-soluble nitrogen-containing organic material as a driers in the formula. Although the amount was not much, it did act as a sicca. We cut the raw paper made of corrugated cardboard into uniform paper sheets with a size of 120×80mm, and paint them in an amount of 100 grams per square meter of adhesive. Each paperboard is glued from 5 layers of paper and coated. The total amount of the mixture, the control error is in the range of 0.02 g, otherwise the paper change is sticky, and the sticky cardboard is dried at a temperature of 20°C and a humidity of 80%. In the early stage, it is weighed once every 30 minutes. When it is nearly dry, it is weighed every 6 minutes to measure the dry data of pure oxidized starch adhesive, oxidized starch adhesive with driers, and sodium silicate. See Table 2 for details.

The data in Table 2 shows that the binder with driers has better initial drying performance than pure oxidized starch and sodium silicate, and the full dry performance is comparable to that of sodium silicate. Stabilizers were added to the adhesive so that after one and a half months of storage, the fluidity, viscosity, and color remained essentially the same.
V. Actual use
The adhesives produced by this formula have been used in packaging companies in Hunan Province for more than 10 years. The results reflect good results: After 7 minutes, the tear adhesive surface can be fully napped, and no running squatting can be performed after 15 minutes of pressurization. The production process is simple, the cost is low, and the cost savings over water glass is more than 30%. After testing by the Hunan Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau, the average bond strength reached 80N/楞l0cm, exceeding the national standard (58.8N/楞10cm). (Text / Huang Yawen)
We are manufacturer and supplier of Stainless Steel Butter Dish With Lid,Butter Box,Butter Container,Butter Holder,Butter Tray. And we located in Jiangmen, Guangdong, China. If any interested, please contact us for free.
Butter Dish With Lid,Butter Box,Butter Container,Butter Holder,Butter Tray
Jiangmen Xinhui Zhancha Metal Products Co,. Ltd. , https://www.zcfoodmill.com